SWINE FLU
Dr Partho P Bose, MD, DTCD, DNB, FCCP, FISDA
Chest, Critical Care and Sleep Physician
Founder SAANS foundation
Chairman, SAKSHAM
Sr Consultant, National Heart Institute
Sr Consultant, Max Superspeciality Hospital
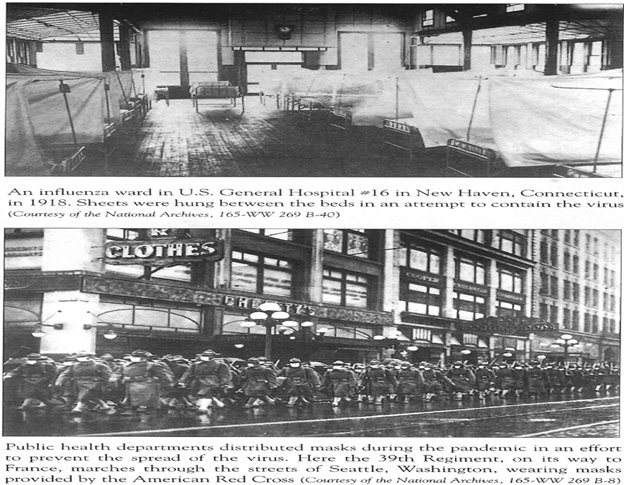
In 1918, an estimated forty million people died as a virus swept the world almost overnight. Even the young and healthy were affected, leaving children orphaned and families devastated. But perhaps the most frightening thing of all was that the killer was a strain of virus that comes around every year and that most people take for granted - FLU
What is Flu?
Flu is an acute respiratory illness caused by infection with influenza viruses.
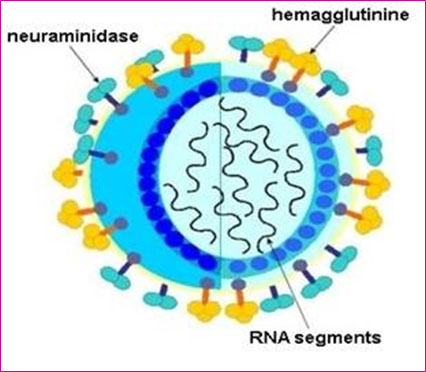
What is Flu/influenza?
- The illness affects the upper and lower respiratory tract and is often accompanied by systemic signs and symptoms such as fever, headache, myalgia, and weakness.
- The disease usually spreads in certain periods of the year, especially winter or early spring.
- When healthy people catch influenza, the disease is self-limiting and usually disappears in about one week. In contrast, influenza can cause serious complications and even death in people at risk of complications.
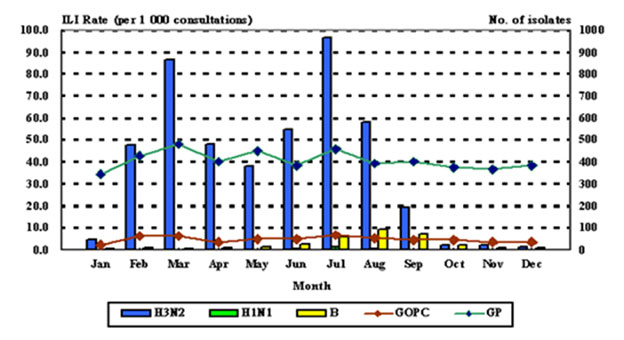
Disease trend
The disease is more common in periods from January to March; and from July to August
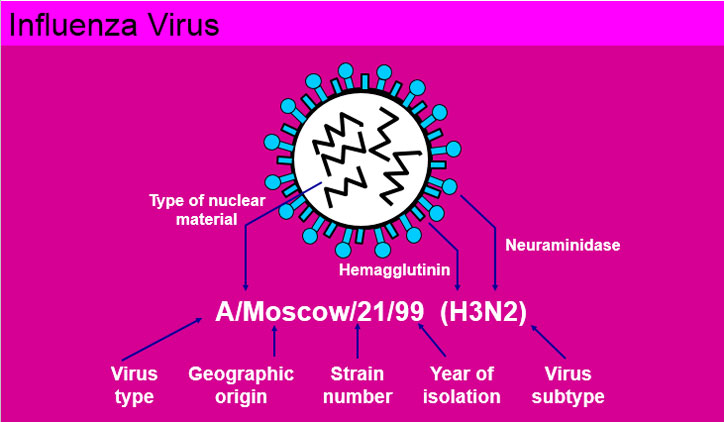
Emergence of Antigenic Sub types of Influenza A virus associated with Pandemic or Epidemic disease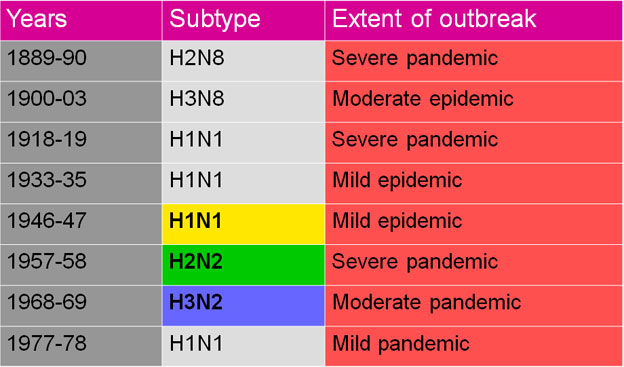
- The most extensive and severe outbreaks are caused by influenza A viruses, in part because of the remarkable propensity of the H and N antigens of these viruses to undergo periodic antigenic variations.
- Major antigenic variations called Antigenic Shift; may be associated with pandemics and are restricted to influenza A viruses.
- Minor variations are called Antigenic Drifts.
Influenza Pandemic
 3 pre-requisites for the start of an Influenza Pandemic
3 pre-requisites for the start of an Influenza Pandemic
- A novel influenza virus subtype emerges and humans in general have no immunity against it
- The new virus must be able to replicate in humans and cause serious illness
- The new virus must be efficiently transmitted from one human to another
How do influenza pandemics arise?
- Fowl are natural reservoirs of influenza and can spread the virus to other birds
- All human influenza viruses arise from avian viruses
- Avian influenza viruses evolve into new strains capable of infecting humans
- A new avian-derived flu virus that can reproduce and spread in humans leads to a pandemic
Influenza: Clinical features
- Incubation period is usually 2 days (range is 1-5 days)
- Severity of illness depends on prior influenza exposure
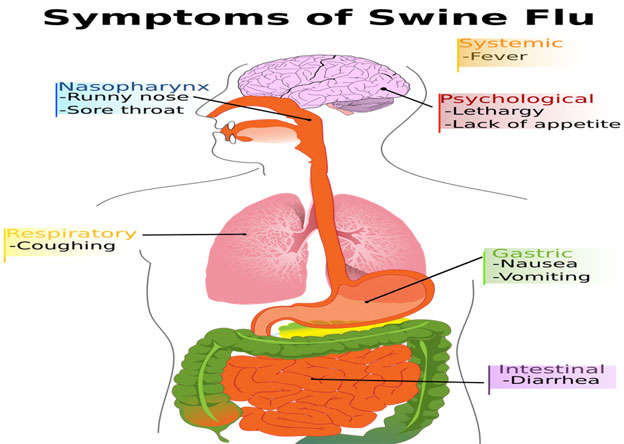
- Abrupt onset includes fever, muscle aches, sore throat, dry cough, and headache
Symptoms of influenza
The first indication of influenza activity in a community is an increase in the number of children with febrile respiratory illnesses who present for medical attention. This increase is followed by increases in rates of influenza like illnesses among adults and eventually by an increase in hospital admissions for patients with pneumonia; worsening of CCF; and exacerbations of COPD
Complications of influenza
Lungs
- Elderly people and chronic cardio-respiratory; diabetic; renal and immune compromised patients.
Pneumonia
- Primary pneumonia
- Secondary pneumonia: Streptococcus pneumoniae, S aureus and H. influenzae.
- Exacerbation of chronic obstructive lung disease.
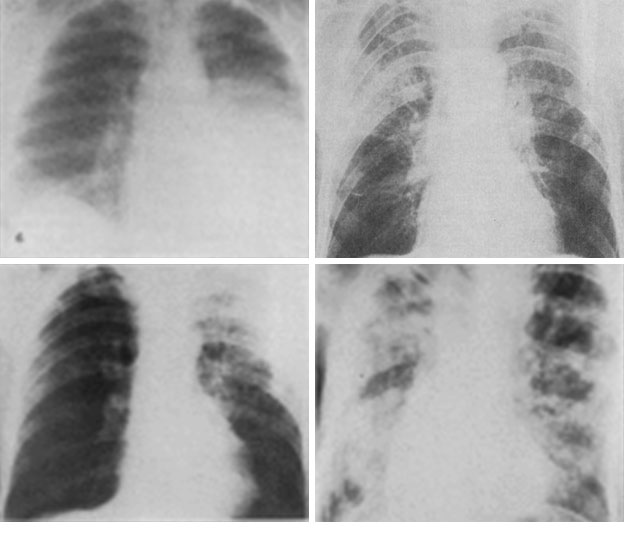
- The most life-threatening of these is pneumonia. If not resolved, death may result from obstruction of air flow to the lungs, arrhythmias of the heart, blood poisoning and shock.
- Rapid onset of high fever and the progression of cough to severe shortness of breath, and bluish discoloration of skin and lips are consistent with a diagnosis of severe
Complications of influenza
Extra Pulmonary complications
Heart
- Myocarditis and pericarditis.
- ECG changes are caused by exacerbation of the underlying heart disease rather than by a direct effect of the influenza virus on the heart muscle
Complications of influenza
- Inflammation (myositis) and destruction of skeletal muscles
- Involvement of muscles has been reported most commonly after influenza B infection of children. Leg pains and muscle tenderness last for 1-5 days. Destruction of the skeletal muscles may result in acute renal failure. Specific treatment may be necessary.
- Central nervous system
- Inflammation of the spinal cord and brain rarely occurs (encephalitis). Mania and schizophrenia were associated with the 1918 influenza pandemic
- GB syndrome
Complications of influenza
Reyes syndrome
Reye’s syndrome causes fatty accumulation in the organs of the body, especially the liver. This is a rare liver and central nervous system complication seen after viral infections, in particular influenza B, almost exclusively occurring in children, and linked with use of salicylates (aspirin). Symptoms are a change in mental status, nausea and vomiting due to edema of the brain. It may be fatal in up to 40% of cases
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Fatigue and a lack of energy that persist after influenza symptoms are gone. People may take several weeks to fully recover, although no cause for the symptoms has been identified.
Lab Finding
- Tissue culture and chick embryo
- Virus may be isolated from throat swab, sputum within 48 – 72 hours after inoculation.
- Rapid viral test
- Detect viral nucleoprotein or neuraminidase by either immunofluorescence, CF or HI techniques. Four fold or greater titer rises by HI or CF or ELISA (60-90% sensitivity and specificity)
Treatment of influenza
- Specific Antiviral therapy
- Amantadine and Rimantadine for influenza A
- Start within 48 hours, and reduction of symptoms by 50%. Dose 200 mg/d for 3-7 days
- Zanamivir and Oseltamivir for both influenza A and B
- Zanamivir, inhaled orally, 10 mg twice a day for 5 days
- Oseltamivir, ingested orally 75 mg twice a day for 5 days. Reduction in duration of signs and symptoms by 1 – 1.5 days.
- Antibacterial therapy for complications
How to prevent Influenza?
‘Influenza pandemic’ Vs ‘Seasonal Influenza’
When compared to localized “seasonal” influenza epidemic, the influenza pandemic:
Spreads quicker and broader
Usually associates with higher severity of illness and a higher death toll
Has more serious consequences, greater social and economic impact
Preparedness Plan for Influenza Pandemic
The Government’s 3-tier response system for handling major infectious disease outbreaks
- Alert Response Level
- Serious Response Level
- Emergency Response Level
Actions from Public – Alert Level
Maintain normal way of life
Pay attention to further announcements from the Government
Actions from Public – Serious Level
- Maintain normal way of life
- Prepare enough masks for possible exigencies
- Pay attention to and comply with guidelines issued by the Government
Emergency Response Level
- Evidence of efficient human-to-human
- Influenza pandemic
Actions from Public – Emergency Level
- Use mask appropriately
- Pay attention to and comply with guidelines issued by the Government
How to Prevent
- Avoid touching live birds and poultry and their droppings
- After contact with live birds and poultry, wash hands thoroughly with liquid soap and water immediately
- Poultry and eggs should be thoroughly cooked before eating
- Travelers’ returning from areas with reported avian flu outbreaks should consult doctors promptly if they have symptoms of influenza after the trip. Let the doctors know the travel history and wear a mask to prevent spread of the disease
- Ensure good ventilation
- Avoid visiting crowded places with poor ventilation
- Prevent the trap of drainage pipe from drying and disinfect drain outlets. Pour half a litre of water into each drain outlet and add 1 easpoon of 1:99 diluted household bleach solution into the outlet once a week
- Keep your home clean, wipe furniture and toilet with 1:99 diluted household bleach solution once a week
8 Steps to Protect Yourself
- Individual preparedness
- Before the pandemic comes
- When the pandemic comes

Step 2 Keep hands Clean
When Should We Wash Our Hands?
Before touching eyes, mouth & nose
When hands are contaminated by
e.g. after coughing / sneezing
- After touching public installations
- or equipment
e.g. escalator handrails, elevator control panels, door knobs
- Before handling food or eating
- After going to toilet
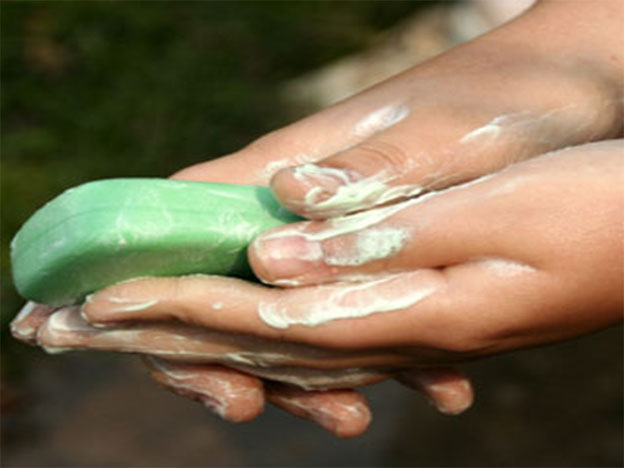 Six steps of Hand washing
Six steps of Hand washing
Step 3 Get Vaccinated
 Seasonal peaks : Jan – Mar / Jul – Aug
Seasonal peaks : Jan – Mar / Jul – Aug- Influenza vaccination one of the effective means of preventing influenza complications
- Influenza vaccination is recommended to special groups
Step 2 : Get Vaccinated
People who should receive influenza vaccination:
 Elderly persons living in
Elderly persons living in- residential care homes
- Long-stay residents of
- institutions for the disabled
- Elderly persons aged 65 years
- or above
- Persons with chronic illnesses
- Health care workers
- Poultry workers
- Children aged 6 to 23 months
- Pregnant women in their second or third trimester
Influenza vaccine can be given on the same day as other types of vaccines
Step 2 : Get Vaccinated
 People not suitable to receive influenza vaccination:
People not suitable to receive influenza vaccination:
- Allergic to eggs, neomycin, etc
- Allergic to previous dose of influenza vaccine
- With bleeding disorders or on warfarin
- Suffer from acute febrile illness
2 Vaccination
- Two weeks after vaccination
- antibodies develop and provide protection
- Immunity declines over time
 Step 4 : Use Mask Properly
Step 4 : Use Mask Properly
People who should wear masks:
- Patients with respiratory infection symptoms
- Caregivers of patients with respiratory infection symptoms
- Visitors of clinics or hospitals
Step 4 : Use Mask Properly
 Points to note about wearing a surgical mask :
Points to note about wearing a surgical mask :
- The mask should fit snugly over the face
- Try not to touch the mask once it is secured on your face. If you must do so, wash your hands before and after touching the mask
- When taking off the mask, avoid touching the outside of the mask
Step 5 : Know How Influenza Presents
 Incubation period: about 1-3 days Signs and symptoms of influenza:
Incubation period: about 1-3 days Signs and symptoms of influenza:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle ache
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny nose
Step 6 : Manage Fever Well
 FEVER -
FEVER - Symptom of underlying illness
(we should be concerned about the specific illness that causes fever)
Normal body temperature
- 37℃ / 98.6℉
- can vary 1℃- 1.5℃ normally
Readings taken as reference under different methods of measurement:
- Rectal temperature (38℃)
- Oral or tympanic temperature (37.5 ℃)
- Axillary temperature (37.0 ℃, less reliable)
 Step 7 : Practise Healthy Lifestyle
Step 7 : Practise Healthy Lifestyle
Is one of the most effective ways to prevent communicable diseases
To lead a healthy lifestyle:
 Eat a balanced diet
Eat a balanced diet- Get regular exercise
- Do not smoke
- Have adequate rest
build up body resistance
 Step 8 : Be Resourceful
Step 8 : Be Resourceful
Influenza Vaccine – CDC guidelines
Types of vaccines
FLU SHOT
An inactivated vaccine (containing killed virus) that is given with a needle, usually in the arm. The flu shot is approved for use in people older than 6 months, including healthy people and people with chronic medical conditions.
NASAL SPRAY FLU VACCINE
A vaccine made with live, weakened flu viruses that do not cause the flu (sometimes called LAIV for “Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine”). LAIV (FluMist®) is approved for use in healthy people 2-49 years of age* who are not pregnant.
Influenza Vaccine – CDC guidelines
Types of vaccines
- Each vaccine contains three influenza viruses-one A (H3N2) virus, one A (H1N1) virus, and one B virus. The viruses in the vaccine change each year based on international surveillance and scientists’ estimations about which types and strains of viruses will circulate in a given year.
- About 2 weeks after vaccination, antibodies that provide protection against influenza virus infection develop in the body.
Influenza Vaccine
| Trivalent | Type A (2) and type B (1) |
| Efficacy | Varies depending on circulating strain, age, and underlying illness |
| Immunity | < 1 year |
| Schedule | One dose annually |
Influenza Vaccine – CDC guidelines
When to get vaccinated
- October or November is the best time to get vaccinated, but you can still get vaccinated in December and later.
- Flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May
- In general, anyone who wants to reduce their chances of getting the flu can get vaccinated.
- However, it is recommended by ACIP that certain people should get vaccinated each year. They are either people who are at high risk of having serious flu complications or people who live with or care for those at high risk for serious complications.
People at high risk from complications from the flu:
- Children aged 6 months until their 5th birthday
- Pregnant women
- People 50 years of age and older
- People of any age with certain chronic medical conditions
- People who live in nursing homes and other long term care facilities
People who live with or care for those at high risk for complications from flu, including:
- Household contacts of persons at high risk for complications from the flu.
- Household contacts and out of home caregivers of children less than 6 months of age (these children are too young to be vaccinated)
- Healthcare workers.
- People who have a severe allergy to chicken eggs.
- People who have had a severe reaction to an influenza vaccination in the past.
- People who developed Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) within 6 weeks of getting an influenza vaccine previously.
- Influenza vaccine is not approved for use in children less than 6 months of age.
- People who have a moderate or severe illness with a fever should wait to get vaccinated until their symptoms lessen.
Vaccine effectiveness
- The ability of flu vaccine to protect a person depends on the age and health status of the person getting the vaccine, and the similarity or “match” between the virus strains in the vaccine and those in circulation.
- Testing has shown that both the flu shot and the nasal-spray vaccine are effective at preventing the flu.
Vaccine Efficiency
| 70-90% | For persons < 65 years of age |
| 30-40% | For the frail, elderly |
| 50-60% | Preventing hospitalization |
| 80% preventing death | Preventing death |
Vaccine Side effects
- The flu shot: The viruses in the flu shot are killed (inactivated), so you cannot get the flu from a flu shot. Some minor side effects that could occur are
- Soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given
- Fever (low grade)
- Aches
- If these problems occur, they begin soon after the shot and usually last 1 to 2 days. Almost all people who receive influenza vaccine have no serious problems from it.





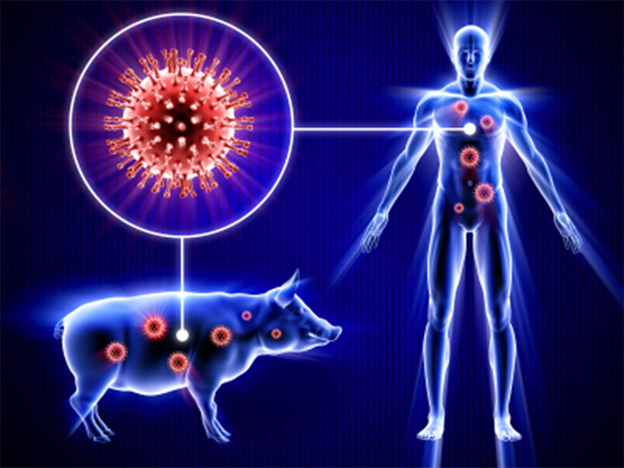













 3 pre-requisites for the start of an Influenza Pandemic
3 pre-requisites for the start of an Influenza Pandemic




 Six steps of Hand washing
Six steps of Hand washing
 Seasonal peaks : Jan – Mar / Jul – Aug
Seasonal peaks : Jan – Mar / Jul – Aug Elderly persons living in
Elderly persons living in Step
Step Points to note about wearing a surgical mask :
Points to note about wearing a surgical mask : Incubation period:
Incubation period: FEVER
FEVER Step
Step Eat a balanced diet
Eat a balanced diet Step 8 : Be Resourceful
Step 8 : Be Resourceful

